
Pulumiとは
使い慣れたプログラミング言語を使用してインフラストラクチャコードを作成します。
オートコンプリート、型チェック、ドキュメントを備えた IDE を使用して、インフラストラクチャを定義するステートメントを作成します。
はじめに
PulumiのIaCコードは、様々な言語で出力することができます。
本記事では、Pythonで出力してみました。
所感
今のところ、使い勝手はTerraformと変わりはなさそうという感触。
SaaSのPulumi Cloudの利用が必須で、そこでterraformでいうtfstateを管理している。
Pythonなどの言語でIaCコードを書けるので、開発者には向いているかもしれない。
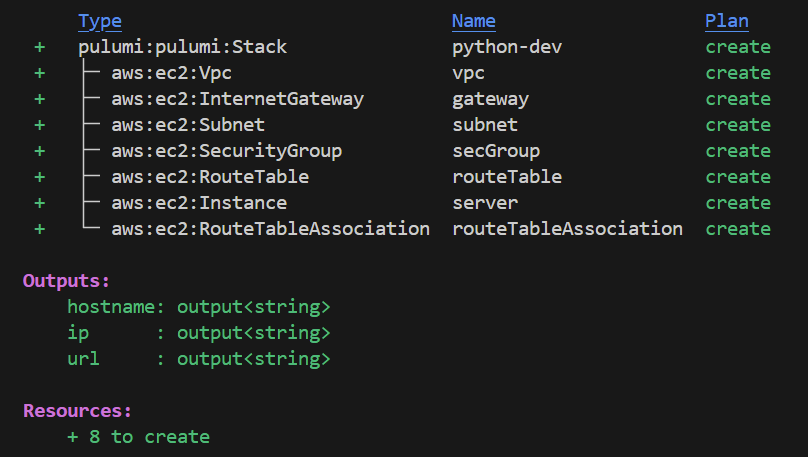
単一のWebサーバを構築するコード
以下のリソースを作成するコードです。
IaC触ったことがある人は、Python知らなくても何となく読める気がします。
$ cat __main__.py import pulumi import pulumi_aws as aws # Get some configuration values or set default values. config = pulumi.Config() instance_type = config.get("instanceType") if instance_type is None: instance_type = "t3.micro" vpc_network_cidr = config.get("vpcNetworkCidr") if vpc_network_cidr is None: vpc_network_cidr = "10.0.0.0/16" # Look up the latest Amazon Linux 2 AMI. ami = aws.ec2.get_ami(filters=[aws.ec2.GetAmiFilterArgs( name="name", values=["amzn2-ami-hvm-*"], )], owners=["amazon"], most_recent=True).id # User data to start a HTTP server in the EC2 instance user_data = """#!/bin/bash echo "Hello, World from Pulumi!" > index.html nohup python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80 & """ # Create VPC. vpc = aws.ec2.Vpc("vpc", cidr_block=vpc_network_cidr, enable_dns_hostnames=True, enable_dns_support=True) # Create an internet gateway. gateway = aws.ec2.InternetGateway("gateway", vpc_id=vpc.id) # Create a subnet that automatically assigns new instances a public IP address. subnet = aws.ec2.Subnet("subnet", vpc_id=vpc.id, cidr_block="10.0.1.0/24", map_public_ip_on_launch=True) # Create a route table. route_table = aws.ec2.RouteTable("routeTable", vpc_id=vpc.id, routes=[aws.ec2.RouteTableRouteArgs( cidr_block="0.0.0.0/0", gateway_id=gateway.id, )]) # Associate the route table with the public subnet. route_table_association = aws.ec2.RouteTableAssociation("routeTableAssociation", subnet_id=subnet.id, route_table_id=route_table.id) # Create a security group allowing inbound access over port 80 and outbound # access to anywhere. sec_group = aws.ec2.SecurityGroup("secGroup", description="Enable HTTP access", vpc_id=vpc.id, ingress=[aws.ec2.SecurityGroupIngressArgs( from_port=80, to_port=80, protocol="tcp", cidr_blocks=["0.0.0.0/0"], )], egress=[aws.ec2.SecurityGroupEgressArgs( from_port=0, to_port=0, protocol="-1", cidr_blocks=["0.0.0.0/0"], )]) # Create and launch an EC2 instance into the public subnet. server = aws.ec2.Instance("server", instance_type=instance_type, subnet_id=subnet.id, vpc_security_group_ids=[sec_group.id], user_data=user_data, ami=ami, tags={ "Name": "webserver", }) # Export the instance's publicly accessible IP address and hostname. pulumi.export("ip", server.public_ip) pulumi.export("hostname", server.public_dns) pulumi.export("url", server.public_dns.apply(lambda public_dns: f"http://{public_dns}")) $
環境構築&プロジェクト作成
前回同様、VScodeのDevcontainerでPulumiのコンテナイメージを使用しています。 環境はGitHubに上げています。
まず、適当なディレクトリを作成し、移動します。
次に、pulumi new aws-pythonを実行します。これが便利で、プロジェクトの作成はもちろん、必要なpkgのインストールも実行してくれました。
なお、Purumiコマンドの初回実行時の場合は、アクセストークンの入力が必要です。
$ mkdir get_started/python $ cd get_started/python/ $ $ pulumi new aws-python This command will walk you through creating a new Pulumi project. Enter a value or leave blank to accept the (default), and press <ENTER>. Press ^C at any time to quit. project name (python): // ブランクのままエンターを推すと、(デフォルト値)が入る project description (A minimal AWS Python Pulumi program): Created project 'python' Please enter your desired stack name. To create a stack in an organization, use the format <org-name>/<stack-name> (e.g. `acmecorp/dev`). stack name (dev): // エンター Created stack 'dev' aws:region: The AWS region to deploy into (us-east-1): ap-northeast-1 // 東京リージョンを指定 Saved config Installing dependencies... Creating virtual environment... Finished creating virtual environment Updating pip, setuptools, and wheel in virtual environment... (略) Downloading attrs-23.2.0-py3-none-any.whl (60 kB) ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 60.8/60.8 kB 59.0 MB/s eta 0:00:00 Downloading typing_extensions-4.10.0-py3-none-any.whl (33 kB) Installing collected packages: arpeggio, typing-extensions, six, semver, pyyaml, protobuf, grpcio, dill, attrs, pulumi, parver, pulumi-aws Successfully installed arpeggio-2.0.2 attrs-23.2.0 dill-0.3.8 grpcio-1.60.1 parver-0.5 protobuf-4.25.3 pulumi-3.111.1 pulumi-aws-6.27.0 pyyaml-6.0.1 semver-2.13.0 six-1.16.0 typing-extensions-4.10.0 Finished installing dependencies Finished installing dependencies Your new project is ready to go! To perform an initial deployment, run `pulumi up` $
Pythonで出力したIaCコード
作成された各ファイルを確認していきます。
$ ls -la total 0 drwxr-xr-x 1 vscode vscode 512 Apr 30 12:45 . drwxr-xr-x 1 vscode vscode 512 Apr 30 12:42 .. -rw-r--r-- 1 vscode vscode 12 Apr 30 12:45 .gitignore -rw-r--r-- 1 vscode vscode 37 Apr 30 12:45 Pulumi.dev.yaml -rw-r--r-- 1 vscode vscode 186 Apr 30 12:45 Pulumi.yaml -rw-r--r-- 1 vscode vscode 219 Apr 30 12:45 __main__.py -rw-r--r-- 1 vscode vscode 46 Apr 30 12:45 requirements.txt drwxr-xr-x 1 vscode vscode 512 Apr 30 12:45 venv $ ls -l ./venv/ total 0 drwxr-xr-x 1 vscode vscode 512 Apr 30 12:48 bin drwxr-xr-x 1 vscode vscode 512 Apr 30 12:45 include drwxr-xr-x 1 vscode vscode 512 Apr 30 12:45 lib lrwxrwxrwx 1 vscode vscode 3 Apr 30 12:45 lib64 -> lib -rw-r--r-- 1 vscode vscode 76 Apr 30 12:45 pyvenv.cfg $
- Pulumi.yaml
$ cat Pulumi.yaml name: python runtime: name: python options: virtualenv: venv description: A minimal AWS Python Pulumi program config: pulumi:tags: value: pulumi:template: aws-python $
$ cat Pulumi.dev.yaml config: aws:region: ap-northeast-1
- requirements.txt
$ cat requirements.txt pulumi>=3.0.0,<4.0.0 pulumi-aws>=6.0.2,<7.0.0
$ cat __main__.py
"""An AWS Python Pulumi program"""
import pulumi
from pulumi_aws import s3
# Create an AWS resource (S3 Bucket)
bucket = s3.Bucket('my-bucket')
# Export the name of the bucket
pulumi.export('bucket_name', bucket.id)
Pulumi CloudでプロジェクトをYaml出力と比較したところ、言語の違いだけでこれといった差異はありませんでした。
スタックのデプロイ
pulumiコマンドで、リソースを作成します。
$ pulumi up Previewing update (dev) View in Browser (Ctrl+O): https://app.pulumi.com/mito-201/python/dev/previews/*** Type Name Plan + pulumi:pulumi:Stack python-dev create + └─ aws:s3:Bucket my-bucket create Outputs: bucket_name: output<string> Resources: + 2 to create Do you want to perform this update? yes Updating (dev) View in Browser (Ctrl+O): https://app.pulumi.com/mito-201/python/dev/updates/1 Type Name Status + pulumi:pulumi:Stack python-dev created (5s) + └─ aws:s3:Bucket my-bucket created (2s) Outputs: bucket_name: "my-bucket-e5e00c1" Resources: + 2 created Duration: 9s $
スタックのデストロイ
pulumiコマンドで、作成したリソースを削除します。
$ pulumi destroy Previewing destroy (dev) View in Browser (Ctrl+O): https://app.pulumi.com/mito-201/python/dev/previews/e75bfeab-cb2b-4086-b33b-22a0d77bad9e Type Name Plan - pulumi:pulumi:Stack python-dev delete - └─ aws:s3:Bucket my-bucket delete Outputs: - bucket_name: "my-bucket-e5e00c1" Resources: - 2 to delete Do you want to perform this destroy? yes Destroying (dev) View in Browser (Ctrl+O): https://app.pulumi.com/mito-201/python/dev/updates/2 Type Name Status - pulumi:pulumi:Stack python-dev deleted (0.49s) - └─ aws:s3:Bucket my-bucket deleted (0.81s) Outputs: - bucket_name: "my-bucket-e5e00c1" Resources: - 2 deleted Duration: 4s The resources in the stack have been deleted, but the history and configuration associated with the stack are still maintained. If you want to remove the stack completely, run `pulumi stack rm dev`. $
Pulimi Cloudのスタックの削除
Pulimi Cloudにはスタックが残っているので、pulumi stack rm devで完全に削除します。
なお、IaCコードファイルは残ります。
$ pulumi stack rm dev This will permanently remove the 'dev' stack! Please confirm that this is what you'd like to do by typing `dev`: dev Stack 'dev' has been removed! $ $ ls Pulumi.yaml __main__.py __pycache__ requirements.txt venv $
その他
AWSクレデンシャルを登録しなかった場合のエラー
この程度のエラーであれば分かりやすいです。対応方法も提示されています。
error: pulumi:providers:aws resource 'default_6_32_0' has a problem: No valid credential sources found.
$ pulumi up Previewing update (dev) View in Browser (Ctrl+O): https://app.pulumi.com/mito-201/python/dev/previews/b74b3442-46fc-4bf7-955f-5aed8248d705 Downloading plugin: 229.75 MiB / 229.75 MiB [======================] 100.00% 23s [resource plugin aws-6.32.0] installing Type Name Plan Info + pulumi:pulumi:Stack python-dev create └─ pulumi:providers:aws default_6_32_0 1 error Diagnostics: pulumi:providers:aws (default_6_32_0): error: pulumi:providers:aws resource 'default_6_32_0' has a problem: No valid credential sources found. Please see https://www.pulumi.com/registry/packages/aws/installation-configuration/ for more information about providing credentials. NEW: You can use Pulumi ESC to set up dynamic credentials with AWS OIDC to ensure the correct and valid credentials are used. Learn more: https://www.pulumi.com/registry/packages/aws/installation-configuration/#dynamically-generate-credentials